5G home internet vs. cable comparison guide
In the debate of 5G home internet vs. cable, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but there are some key distinctions. If you’re sussing out whether the newcomer to home internet technology will give you the home internet performance you need, check out this guide for a point-by-point comparison with cable.
5G vs. cable internet: reliability
- 5G. The wireless technology powering your mobile phone is the same one that powers 5G home internet. Historically, wireless technologies haven’t had the same reliability as wired networks, but with its close-range towers, 5G is narrowing that gap. Plus, despite being a newer technology that’s already contending with wired services on key indicators, 5G performance still has room to improve—and it’s improving all the time.
- Cable. Cable internet relies on underground networks of coaxial cables to deliver broadband to your home. These wired lines can make your internet signal more consistent than 5G, but that edge may be less noticeable if you connect your devices via Wi-Fi (also a radio wave technology) rather than an Ethernet cable.
5G home internet vs. cable: speed
Whether your household spends an average weeknight streaming TV, gaming with buddies, catching up on work, or getting digital facetime with Mom, more speed lets you multitask with less impact on your internet performance.
- 5G. Home 5G internet speeds vary by provider and by area. Typically, Verizon 5G Home Internet plan speeds run up to 100 Mbps, up to 150 Mbps, and up to 300 Mbps depending on your plan—though in high-band areas, they can exceed these speeds and even reach up to 1 Gbps on the fastest plan. Upload speeds run up to 10, 15, and 20 Mbps typically, but they can reach 75 Mbps in select areas.
- Cable. Cable speeds run comparable to 5G speeds on the more affordable end of the scale. On the fastest plans, maximum wired speeds can run as fast as multiple gigs, but the more popular plans hover closer to 5G speeds. Cable upload speeds vary but run similar to 5G upload speeds, even in packages with faster downloads.
Speeds valid as of date of publication. 5G Home Internet plans vary depending on address/location, equipment, network connection, and external factors affecting cellular networks. Visit https://www.verizonspecials.com/5g-home-internet and https://www.verizon.com/about/our-company/network-performance for the latest information.
5G home internet vs. cable: latency
Latency measures the delay that can make your internet feel slow even if you have enough speed. When you hold frequent video calls, work from cloud apps all day, or have online teammates depending on you, you need that responsive and dependable performance.
- 5G. Latency can vary based on proximity to a 5G tower and local network load, but in many areas, it’s quick and on par with cable. In Verizon 5G Ultra Wideband areas, typical latency runs 37–70 ms—and even in rural areas relying on 4G/LTE coverage, latency runs 49–75 ms.
- Cable. Cable offers low latencies and reliable performance in most areas (though not as pristine as that of 100% fiber networks) and is vulnerable to slowdowns during network congestion.
5G home internet vs. cable: installation
- 5G. You’ll never need professional installation with 5G home internet because radio-wave transmission eliminates the need for physically connecting your equipment to your provider’s network. All you need to get started is an easy setup kit for your new 5G gateway, which functions just like a cable modem.
- Cable. Unless you move into a newly built home or want to install your cable hookup in a different spot, you probably won’t need professional installation. However, unlike 5G, cable might require onsite technician visits down the line for connectivity problems, for example if the line to your home ever gets damaged.
5G home internet vs. cable: availability
- 5G. Wireless 5G home internet is rapidly expanding to cities and suburbs nationwide. It’s harder to deliver to rural areas since 5G towers have to be closer together than previous cell technologies. That said, home internet from 4G/LTE bands is available in many rural areas instead, providing vital connectivity that’s usually more affordable than competing satellite plans.
- Cable. Cable is widely available in cities, suburbs, and smaller towns in the middle of a growth spurt. It’s hard to come by in rural areas, where the population density is too low to make the infrastructure cost effective.

5G home internet vs. cable: pricing
Regardless of provider, home internet pricing tends to be best when you bundle. It’s hard to make blanket comparisons about price otherwise, because offers and terms vary so much by provider, plan, and service area.
Verizon 5G Home Internet plans start at $35/month with Auto Pay and any Verizon mobile plan, and your rate includes a wireless router and is guaranteed for 3 years. The upgraded plans come with faster speeds—and prices guaranteed even longer.
Pricing valid as of date of publication. Visit https://www.verizonspecials.com/5g-home-internet for the latest information
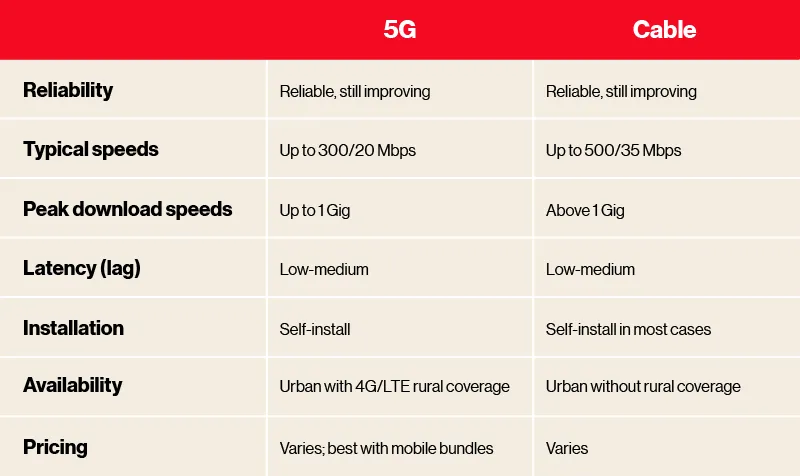
5G home internet vs. cable, at a glance
There you have it: the key differences between 5G and cable. Keep in mind that all this information varies by provider and even by address, so make sure to check current offers in your area.
The bottom line: 5G home internet vs. cable
Unless you’re confident that you want multi-gig home internet, 5G holds its own against cable. Plus—if you’re certain you want multi-gig, there’s no question that 100% fiber performs better than cable. Check your area for Verizon Fios availability now.
But hey, if you want home internet from those who have been shaping the wireless game since the year 2000, choose 5G home internet—and choose Verizon.